Sustainable Practices for English Gardens: Modern Approaches to Historical Artisanship
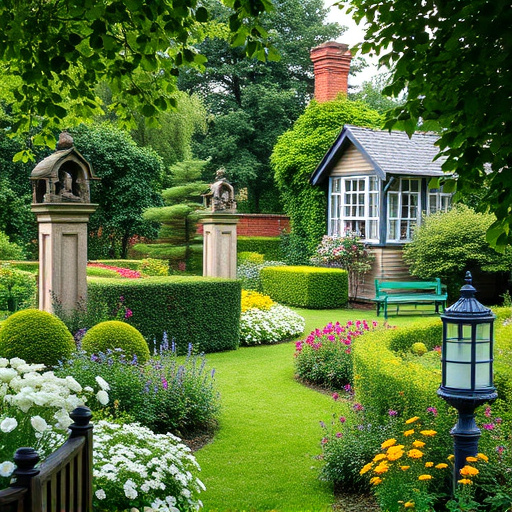
English gardens have evolved from medieval food production and status symbols to modern eco-friendly…….
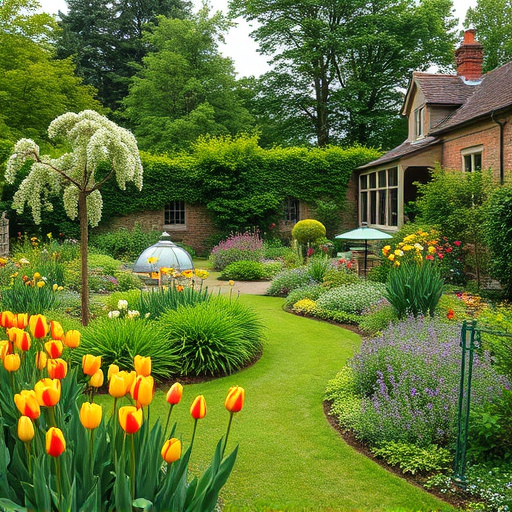

English gardens have evolved from medieval food production and status symbols to modern eco-friendly oases. Influenced by French and Italian styles, they became known for formal symmetry. Today, English gardens embrace sustainability with organic farming, wildlife conservation, and water efficiency, using native plants and eco-conscious practices like composting and drip irrigation. These changes ensure healthier ecosystems, vibrant blooms, and reduced environmental impact, making English gardens more resilient and beautiful than ever.
England’s rich gardening history has shaped a unique landscape of picturesque landscapes and diverse ecosystems. In contemporary times, there’s a growing emphasis on sustainable practices among English gardeners, driven by environmental consciousness. This article explores this evolution, offering insights into the core principles, plant choices, water conservation methods, and organic waste management strategies that define modern, eco-friendly english gardens.
- Understanding English Gardens: A Historical Perspective
- Embracing Sustainability: Key Principles for Modern Gardening
- Eco-Friendly Plant Choices and Their Benefits
- Water Conservation Techniques for English Gardens
- Organic Waste Management: Closing the Loop in Your Garden
Understanding English Gardens: A Historical Perspective

English gardens have a rich history deeply intertwined with the country’s cultural and social evolution. Dating back to medieval times, these green spaces have served various purposes, from providing food and medicine in monastic gardens to becoming symbols of status and beauty in private estates. Historically, English gardening practices were heavily influenced by French and Italian styles, particularly during the 17th and 18th centuries, leading to the creation of formal, symmetrical landscapes.
Over time, as environmental consciousness grew, so did the emphasis on sustainable gardening. Today, English gardens embrace eco-friendly practices such as organic farming, wildlife conservation, and water efficiency. This shift reflects a broader global trend towards sustainability, where gardeners and designers prioritize preserving biodiversity, reducing chemical use, and promoting natural ecosystem balance within their green oases.
Embracing Sustainability: Key Principles for Modern Gardening

In England, sustainable gardening practices are gaining traction as folks recognize the importance of eco-friendly approaches to create and maintain lush green spaces. Embracing sustainability means integrating principles that minimize environmental impact while maximizing the health and beauty of gardens. Key principles include using organic fertilizers and pesticides to avoid polluting soil and water, promoting biodiversity by planting a mix of native flora species that support local wildlife, and conserving water through efficient irrigation systems.
Modern gardeners in England are also adopting techniques like composting to reduce waste, mulching to suppress weeds and retain moisture, and choosing plants suited to local climates to decrease the need for excessive resources. These practices not only contribute to a greener planet but also create vibrant, resilient english gardens that thrive in harmony with nature.
Eco-Friendly Plant Choices and Their Benefits

English gardens have embraced sustainable practices, with a significant focus on eco-friendly plant choices. This shift is driven by the desire to protect local ecosystems and promote biodiversity. By selecting native plants, gardeners contribute to the preservation of natural habitats, providing food and shelter for indigenous wildlife. Species such as wildflowers, hedgerow plants, and certain trees offer year-round benefits, attracting bees, butterflies, and birds.
These plant options are not only environmentally beneficial but also aesthetically pleasing and low maintenance. Native plants adapt well to local conditions, reducing the need for excessive watering and chemical fertilizers. They create vibrant, diverse gardens that support ecological balance, ensuring English gardens remain lush oases while minimizing their environmental footprint.
Water Conservation Techniques for English Gardens

English gardens, known for their vibrant blooms and lush landscapes, can embrace sustainable water conservation practices to ensure a greener future. One effective technique is the implementation of drip irrigation systems, which deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste. This method, tailored to the unique needs of each plant, reduces water usage compared to traditional sprinklers.
Additionally, creating water-efficient garden designs encourages natural rainfall harvesting. Perennial plants and native species, adapted to local conditions, require less frequent watering. Creating water features like rain gardens or ponds also helps with drainage while providing habitats for wildlife. These strategies ensure that English gardens remain picturesque without straining local water resources.
Organic Waste Management: Closing the Loop in Your Garden

In the pursuit of sustainable gardening, English gardeners have embraced organic waste management as a holistic approach to closing the loop within their green spaces. This involves transforming organic byproducts, such as vegetable scraps and yard trimmings, into nutrient-rich compost that can be reintroduced into the garden ecosystem. By doing so, gardeners minimize waste sent to landfills while enhancing soil fertility, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
The process typically begins with setting up a composting system tailored to individual needs, ranging from simple pile methods to more structured bins. Once established, these systems naturally decompose organic matter, resulting in a dark, crumbly substance that is an asset to any garden. This organic compost can then be used to enrich the soil, promoting healthy plant growth and contributing to a self-sustaining garden ecosystem characteristic of English gardening excellence.