Adapting English Gardens for Climate Resilience: Strategies and Innovations
English gardens are iconic landscapes that are adapting to the challenges of climate change by inco…….

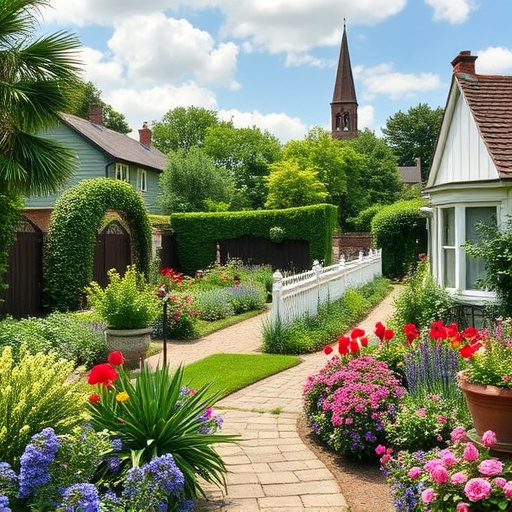
English gardens are iconic landscapes that are adapting to the challenges of climate change by incorporating resilient strategies. Gardeners and landscape designers are embracing sustainable practices such as selecting a diverse range of plant species that can withstand varying climatic conditions, from droughts to extreme weather events. Innovative solutions like automated irrigation systems tailored to soil moisture levels ensure efficient water use, while permeable paving and rain gardens help manage water resources sustainably. Composting enriches the soil, supporting plant health across different environments. These measures are crucial for preserving the ecological richness and aesthetic charm of English gardens, ensuring they remain vibrant and biodiverse in the face of a changing climate. By blending traditional horticulture with modern technology, these timeless spaces can continue to be cherished sanctuaries for both wildlife and people.
English gardens have long been a reflection of the nation’s horticultural heritage and an embodiment of natural beauty. As climate patterns shift, these verdant spaces face new challenges and opportunities for adaptation. This comprehensive article delves into the historical evolution of English gardens in response to climatic changes, highlighting the importance of native plants, water management strategies, and biodiversity to create resilient garden ecosystems. It also explores innovative landscaping techniques and planning for future uncertainties, ensuring that these gardens remain vibrant and sustainable for generations to come.
- Historical Context of English Gardens and Their Evolving Relationship with Climate
- The Role of Native Plants in Adapting to Climatic Changes
- Water Management Strategies for Sustainable English Gardens
- Embracing Biodiversity: Attracting Wildlife Amidst Climate Variability
- Mitigating the Impact of Extreme Weather Events on Garden Ecosystems
- Innovative Landscaping Techniques to Combat Climate Change Effects
- Future-Proofing English Gardens: Planning for Climate Uncertainty
Historical Context of English Gardens and Their Evolving Relationship with Climate

English gardens have a storied history that intertwines with the country’s cultural identity and its evolving relationship with climate. The concept of the English garden dates back to the medieval period, where practicality ruled, and ornamental gardens were a display of wealth and status. Fast forward to the Renaissance, and the influence of Italian and French gardens introduced more formal designs, reflecting the tastes of the aristocracy. However, it was during the 17th century that the English garden truly began to take shape with the advent of the naturalistic style, as seen in the works of landscape architects like Capability Brown and Lancelot ‘Capability’ Brown, who emphasized scenic natural landscapes over formal gardens. This period marked a significant shift from rigid geometric patterns to more organic and flowing designs that harmonized with the natural contours of the land.
The 19th century brought about further transformations, with the introduction of exotic plants from colonial ventures, which expanded the palette of plants available in English gardens. The temperate microclimates within these gardens allowed for a diverse array of flora to thrive, regardless of their geographical origins. As the climate evolved and became more unpredictable due to industrialization and its environmental impact, English gardeners had to adapt, ensuring the resilience of their gardens in the face of new weather patterns and conditions. Today, English gardens continue to evolve as gardeners navigate the challenges presented by changing climates, including the effects of climate change. The focus has shifted towards sustainable practices, native plants, and creating habitats that are not only beautiful but also supportive of local ecosystems and biodiversity. This ongoing adaptation ensures that the legacy of English gardens endures, showcasing a living history that continues to adapt and flourish within the ever-changing tapestry of Britain’s climate.
The Role of Native Plants in Adapting to Climatic Changes

English gardens have historically showcased a diverse array of flora, many of which are native plants that thrive in the region’s specific climatic conditions. As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, these gardens stand at the forefront of climate adaptation. Native plants, with their deep roots and evolutionary resilience, play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of English gardens amidst climatic changes. They are naturally attuned to local environmental factors, making them more robust and less susceptible to the stresses associated with changing weather patterns. By incorporating native species, gardeners can create ecosystems that are self-sustaining and resilient to extreme conditions, thereby reducing the need for intensive irrigation and artificial intervention. These gardens not only conserve water but also support local biodiversity, providing habitats for a variety of wildlife. As such, they serve as living laboratories that demonstrate how traditional gardening practices can evolve with climate considerations, ensuring the continued beauty and viability of English gardens for generations to come. In this context, the strategic use of native plants becomes crucial in adapting to and mitigating the impacts of a changing climate on these treasured landscapes.
Water Management Strategies for Sustainable English Gardens

In the context of English gardens, which have long been celebrated for their intricate designs and diverse plant life, water management strategies play a pivotal role in maintaining sustainable ecosystems within these green spaces. As climate change continues to influence weather patterns, leading to both droughts and intense rainfall events, gardeners are adopting innovative approaches to conserve water while ensuring the health of their gardens. Implementing drip irrigation systems allows for efficient water usage, delivering moisture directly to plant roots and reducing evaporation from open surfaces. Rainwater harvesting is another critical strategy; collecting and storing rainwater not only conserves potable water but also enriches the soil with natural nutrients. Additionally, the use of permeable surfaces and native plants, which are well-adapted to local conditions, can help manage rainfall runoff and reduce the need for supplemental irrigation. By integrating these water management strategies, English gardens can continue to thrive while respecting the environment and adapting to the challenges posed by a changing climate.
Furthermore, the integration of ponds or water features, when designed thoughtfully, can serve as natural water collection points while also providing aesthetic value. These features can help to regulate garden moisture levels, serving as reservoirs that replenish groundwater during dry spells. The use of water-efficient plants and grasses, which are increasingly becoming a staple in sustainable garden design, complements these strategies. By selecting species with low water requirements, English gardens can reduce their overall water footprint without compromising on beauty or biodiversity. These practices not only contribute to the conservation of this precious resource but also ensure that the tradition of English gardening continues to flourish within an ecologically conscious framework.
Embracing Biodiversity: Attracting Wildlife Amidst Climate Variability

In the realm of English gardens, a harmonious blend of horticulture and ecological conservation is increasingly becoming a hallmark of sustainable gardening practices. As climate variability introduces new challenges, gardeners are adopting strategies to embrace biodiversity within their garden spaces. By carefully selecting native plants and flowers that flourish in the local climate, English gardens can serve as vital habitats for a variety of wildlife. These plant choices not only withstand environmental changes but also provide essential resources for pollinators, birds, and other beneficial creatures. The integration of ponds, hedgerows, and meadow areas further enhances these ecosystems, offering diverse microhabitats that support a wide range of species. This approach to gardening aligns with the broader objective of promoting ecological resilience and ensuring that these green spaces continue to thrive amidst climate uncertainties.
Furthermore, the adoption of eco-friendly practices such as composting, avoiding chemical pesticides, and using water wisely contributes to the sustainability of English gardens. These practices minimize the environmental impact and encourage a balanced ecosystem. Gardeners are encouraged to observe and record the wildlife that visits their garden, adopting a ‘citizen science’ approach that benefits both the local environment and scientific understanding of how species adapt to changing conditions. By fostering biodiversity and adapting to climate variability, English gardens can become living examples of ecological stewardship, offering sanctuaries for wildlife and education centers for visitors. This synergy between garden aesthetics, environmental responsibility, and conservation efforts underscores the importance of integrating sustainable practices into the cultivation of these beloved outdoor spaces.
Mitigating the Impact of Extreme Weather Events on Garden Ecosystems

English gardens, with their rich biodiversity and intricate design, can be significantly affected by the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events due to climate change. Gardeners and landscape architects must implement strategies to mitigate these impacts effectively. For instance, integrating a variety of native plant species that are resilient to drought or heavy rainfall can stabilize garden ecosystems. These plants often have evolved adaptations to local conditions, making them more robust in the face of extreme weather. Additionally, the use of permeable surfaces and rain gardens helps manage excessive water during heavy rainfall, preventing soil erosion and reducing the risk of flooding. By designing gardens with sustainable practices in mind, such as water conservation systems and windbreaks, these outdoor spaces can not only survive but also thrive despite the challenges posed by climate variability. This proactive approach ensures that English gardens continue to serve as havens for wildlife and as serene retreats for humans, while also contributing to broader ecological resilience. It is through thoughtful design and ongoing management that these horticultural treasures can endure the test of an ever-changing climate.
Innovative Landscaping Techniques to Combat Climate Change Effects

English gardens, with their rich history and intricate designs, have long been a source of national pride. As climate change continues to alter weather patterns and environmental conditions, gardeners and landscape designers are adapting traditional horticultural practices to ensure these iconic spaces remain resilient and vibrant. Innovative landscaping techniques are being employed to mitigate the effects of extreme weather, from droughts to heavy rainfall. These include the use of native and drought-resistant plants to reduce water usage without compromising the aesthetic appeal that English gardens are known for. Permeable paving and sustainable drainage systems (SuDS) are being integrated to manage surface water more effectively, preventing flooding while maintaining the natural flow of water through the garden. Additionally, the strategic placement of trees, shrubs, and ground covers can provide shade and reduce soil temperature, which in turn helps to conserve moisture.
Furthermore, incorporating biodiversity into English garden designs is another key strategy. By planting a variety of species that support different ecosystems, gardens become more resilient to the impacts of climate change. This approach not only enhances the ecological value of these spaces but also ensures they continue to thrive amidst changing environmental conditions. The use of compost and organic matter enriches the soil, improving its capacity to store carbon and support plant growth. These practices contribute to the overall health of the garden and align with global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As such, English gardens are evolving not just as places of beauty but also as vital green spaces that adapt to and combat the effects of climate change.
Future-Proofing English Gardens: Planning for Climate Uncertainty

The concept of future-proofing English gardens in light of climate uncertainty has become a pressing concern for horticulturists and garden enthusiasts alike. As global weather patterns shift, the traditional elements that define an English garden—lush greenery, varied flora, and serene water features—face new challenges. To adapt to these changes, it is imperative to select plant species that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also resilient to the fluctuating climate conditions. These choices should consider potential temperature extremes, changes in precipitation patterns, and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events. For instance, incorporating drought-resistant plants alongside those that thrive in cooler climates can create a balanced and sustainable garden ecosystem. Additionally, implementing soil improvement techniques, such as composting and organic matter application, enhances the soil’s capacity to retain moisture and support plant health across varying conditions. By integrating climate-responsive design elements and embracing a forward-thinking approach to garden maintenance, English gardens can endure and even flourish in the face of climate uncertainty.
Furthermore, the integration of smart technologies like automated irrigation systems that respond to soil moisture levels can greatly contribute to the sustainability of these gardens. These systems can significantly reduce water usage while ensuring plants receive adequate hydration. Similarly, the use of permeable surfaces and rain gardens helps manage stormwater runoff, mitigating flooding risks and conserving water resources. By embracing both traditional horticultural wisdom and contemporary innovations, English gardens can be designed to not only withstand but also thrive in a changing climate, ensuring their beauty and biodiversity for generations to come.